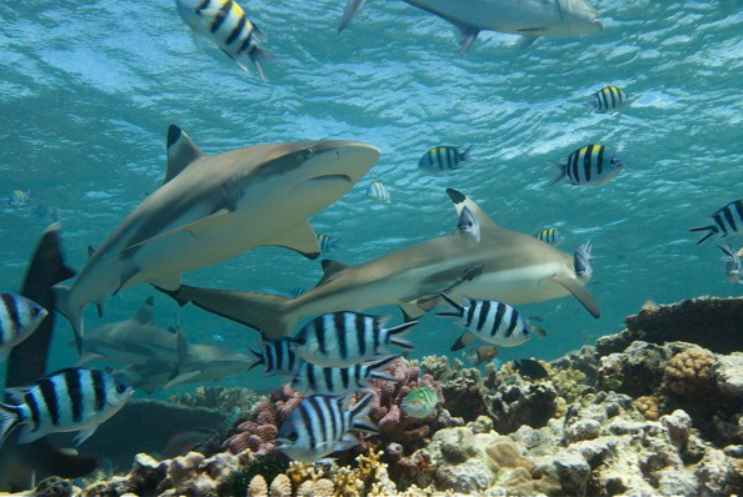
The Persian Gulf’s depths are teeming with life, yet many of its inhabitants remain mysterious. Enter the Gulf Elasmo Project-an ambitious, collaborative research initiative you can explore in detail at gulfelasmoproject.com. Often shortened to GulfElasmoProject or simply Elasmo Project, this endeavor brings together marine biologists, conservationists, and local communities to study and protect one of the Gulf’s most ecologically important groups: the cartilaginous fishes (sharks and rays).
1. Why the GulfElasmoProject Matters
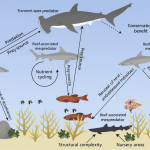
- Ecosystem Balance.
Sharks and rays sit at the top of the marine food chain. By regulating the populations of smaller fish and invertebrates, they help keep coral reefs, seagrass meadows, and mangrove habitats healthy. Without these predators, lower-tier species can proliferate unchecked, triggering a cascade of environmental problems. - Health Indicators.
Cartilaginous fishes are extremely sensitive to changes in water quality. A decline in their numbers-or signs of stress in individuals-often signals pollution, habitat loss, or temperature shifts that could eventually affect entire coastal communities. - Conservation Imperative.
Overfishing, coastal development, and climate change have pushed many shark and ray species toward critical endangerment. The Gulf Elasmo Project aims to generate robust, science-based data to guide sustainable fishing regulations and marine protected area designations.
2. Research Methods
The Elasmo Project employs a multi-pronged approach to study these elusive creatures:
- Field Surveys & Underwater Monitoring
Research vessels deploy baited remote underwater video systems (BRUVS) and acoustic sensors at depths up to 50 m to record shark and ray activity. Divers conduct visual transects, cataloguing individuals by distinctive patterns and scars. - Genetic Sampling
Small tissue biopsies-harmlessly taken from the fins-are analyzed in the lab for DNA barcoding. This reveals population structure, gene flow, and adaptive traits that help certain species survive in changing environments. - Satellite Tagging
Non-invasive satellite tags affixed to larger sharks transmit real-time GPS locations and water temperature data, illuminating their migration routes across the Gulf. - GIS Mapping
All collected data funnel into a Geographic Information System, where migration corridors, nursery grounds, and seasonal hotspots are mapped and publicly shared on gulfelasmoproject.com. - Community Engagement
Local fishermen and coastal communities contribute traditional ecological knowledge through interviews and workshops. Their observations-sometimes spanning generations-fill critical gaps in historical data.
3. Key Achievements to Date
Since its launch in 2020, the Gulf Elasmo Project has delivered remarkable results:
- Identification of over 20,000 individual rays across three key species.
- Discovery of three previously unknown migration corridors, linking offshore feeding grounds to inshore nursery areas.
- Development of genetic markers for early detection of viral and bacterial infections in elasmobranchs.
- Publication of nine peer-reviewed papers in journals such as Marine Ecology Progress Series and Journal of Experimental Biology.
- Establishment of five new marine protected zones based on project recommendations, now under government stewardship.
4. Ecological & Economic Impact
The GulfElasmoProject benefits both nature and people:
- Tourism Growth.
Eco-tourists and recreational divers now flock to the Gulf’s shores, eager to spot sharks in their natural habitat. Shark-watching dives, once niche, are becoming a major draw. - Sustainable Fisheries.
Data-driven catch limits help local fisheries maintain healthy stocks of commercially important species without risking ecosystem collapse. - International Reputation.
Gulf nations leading these conservation efforts bolster their standing as responsible environmental stewards on the global stage.
5. How You Can Get Involved
The Elasmo Project welcomes support from all quarters:
- Volunteer in the Field
Assist with dives, camera deployments, and data logging aboard research vessels. - Financial Support
Sponsor satellite tag purchases, laboratory analyses, or vessel operations. - Academic Partnerships
Contribute expertise, co-author papers, or host student interns through university collaborations. - Outreach & Education
Offer workshops, public lectures, or school programs to raise awareness about shark and ray conservation.
Visit GulfElasmoProject to submit your application or proposal.
6. Frequently Asked Questions
- Where is the project based?
The main research hub operates out of Dubai, with field teams in Abu Dhabi, Sharjah, and Ras Al Khaimah. - How long are typical expeditions?
Field campaigns usually last 3–4 weeks, timed for peak shark and ray activity. - Can I participate remotely?
Yes. The project’s online platform provides access to real-time tracking data, video feeds, and analytical tools you can explore from anywhere.
7. Future Directions
Looking ahead, the Gulf Elasmo Project plans to:
- Implement AI-powered video analysis to automatically identify species and behaviors.
- Deploy autonomous underwater drones for continuous, long-term monitoring.
- Expand study areas into the Oman Sea and southern Iranian waters.
- Launch a marine conservation training center to educate the next generation of Gulf-based scientists.
Conclusion
The Gulf Elasmo Project exemplifies how science, technology, and community engagement can unite to safeguard our oceans. By following their work at gulfelasmoproject.com, you can stay informed, volunteer, or contribute financially. Together, we can ensure that sharks and rays continue to thrive in the Persian Gulf for generations to come.